mild lv hypertrophy Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork . $6,542.00
0 · qrs widening and repolarization abnormality
1 · nice cks left ventricular hypertrophy
2 · mild lv hypertrophy icd 10
3 · lv hypertrophy on echo
4 · left ventricular hypertrophy treatment uk
5 · left ventricular hypertrophy on ecg
6 · left ventricular hypertrophy nice guidelines
7 · eccentric vs concentric lv hypertrophy
$32K+
To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is when the main pumping chamber of the heart becomes thicker and less efficient. It can be caused by high blood pressure, aortic valve stenosis, or other conditions. Learn how .Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to the heart’s .
prada 17ws replica
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which an increase in left ventricular mass occurs secondary to an increase in wall thickness, an increase in left ventricular cavity enlargement, or both. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork .
An enlarged or thickened heart — a condition doctors call left-ventricular (LV) hypertrophy — can lead to heart failure. It also may double the risk of dementia and cognitive impairment . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is an increase in the weight of the left ventricle due to thickening of the left ventricle walls, an increase in space within the left ventricle, or both. The two most common causes of LVH are .Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is sometimes assumed to occur only as a consequence of hypertension. However this is often not the case. LVH is 'an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction and death in men and women with hypertension, and in asymptomatic subjects with normal blood'. The presence of LVH increases the risk of .
For example, the HCM phenotype encompasses patients with differing magnitude of left ventricular (LV) mass, eg, from mild LV wall thickness (≤15 mm) to massive hypertrophy ≥30 mm (arguably the most substantial of any cardiac .In this blog we describe left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and identify the different categories of concentric, eccentric and concentric remodeling. In Part 2 of the blog we will elaborate on LV Mass (LVM) and Relative Wall Thickness (RWT). We will provide step-by-step instructions on how to obtain these values during a routine echocardiogram. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common inherited monogenic cardiac disorder, affecting 0.2-0.5% of the population. 1,2 In the United States, 750,000 people are estimated to have HCM; however, only approximately 100,000 people have been diagnosed, signifying a large gap in the recognition and understanding of this disease. 3 As diagnostic and . Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the muscular heart wall called the septum often becomes thicker than usual. But the thickening can happen anywhere in the left lower heart chamber, also called the left ventricle.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) means that the muscle of the heart's main pump (left ventricle) has become thick and enlarged. This can happen over time if the left ventricle has to work too hard. This part of the heart needs to be strong to pump oxygen-rich blood to your entire body. When the ventricle gets thick, other changes can happen .Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition where the size of the heart muscle is larger than normal. The left ventricle is the heart’s main pumping chamber. It pumps oxygen-rich blood from your heart to the aorta and out to your body. When you have LVH, the muscle wall of the left ventricle becomes thick (hypertrophy) and enlarged.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6. ST elevation in V1-3. Prominent U waves in V1-3.
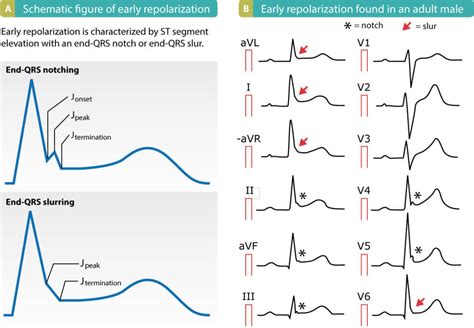
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), as defined by increased LV mass (LVM) on echocardiography, predicts cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients as well as in the general population. 1,2 LVH can occur through ventricular dilatation, wall thickening, or combinations thereof. To distinguish between these patterns of hypertrophy, LVH has been . Mild left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) has been considered as one of the possible structural, physiological adaptations to regular, intensive physical activity. However, it may also appear as one of the subclinical complications of hypertension. In athletes, the differential diagnosis between these two entities may be complicated as regular . It was determined that I had “mild Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)”. Ejection fraction was 54%. MRI indicates heart in “normal range. After wearing a bp monitor for a day hypertension seems to be the cause. I am now taking perindopril erbumine 8 mg daily.
Type 2 Excludes. certain conditions originating in the perinatal period (P04-P96)certain infectious and parasitic diseases ()complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ()congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities ()endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E88)injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external .Prior findings suggest 3.0-7.3% of the population have asymptomatic LV systolic dysfunction (6,8), among whom the majority have mild LV systolic dysfunction (LVEF 45-54%). We observed a 3.5% prevalence of LVEF 50-55%, which reflects a small but significant proportion of the general population.Left ventricular hypertrophy or thickening of the heart muscle is a response to excess stress or workload. It can be associated with hypertension or heart valve disease. . There is mild concentric LV hypertrophy. The diastolic filling .
Background: Individuals with left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy and elevated cardiac biomarkers in middle age are at increased risk for the development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Prolonged . Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. The major conditions associated with LV volume overload are aortic or mitral valve regurgitation and dilated cardiomyopathy.Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a well‐known risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. 1, 2, . Mild attenuation of these associations was seen with additional adjustment for electrocardiographic LVH .
Left ventricular hypertrophy; Right atrial enlargement; Right ventricular enlargement; Ventricular enlargement, right; Clinical Information. Abnormal enlargement of the heart. Enlargement of the heart due to chamber hypertrophy, an increase in wall thickness without an increase in the number of cells (myocytes, cardiac). It is the result of .
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetically determined disease that commonly results in obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), which can produce chest discomfort, dyspnea, fatigue, and syncope. . Mitral Valve Repair for Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy With Mild Septal Hypertrophy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 66:1687. INTRODUCTION. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common finding in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD risk factors and is diagnosed either by electrocardiogram (ECG) or imaging (eg, echocardiography, cardiovascular computed tomography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance [CMR] imaging) []. (See "Left ventricular .
In 1995, Klues HG said that in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the distribution of left ventricular hypertrophy is characteristically asymmetric and particularly heterogeneous, encompassing most possible patterns of wall thickening, from extensive and diffuse to mild and segmental, and with no single morphologic expression considered typical or .Mild left ventricular hypertrophy; Mildly enlarged cardiac chamber; Moderate left ventricular hypertrophy; Moderately enlarged cardiac chamber; Obstruction of pulmonary great vein due to compression by right atrial dilatation; Position of apex beat - finding;Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) develops in response to certain medical conditions that can cause the left ventricle (the lower left chamber of the heart responsible for pumping blood to the body) to work harder than normal. Just like other muscles in your body, when the heart muscle works harder, it gets bigger. . During pregnancy, the requirement for an increased stroke volume and cardiac output is accompanied by a substantial increase in LV dimension and mass, which regresses over months in the postpartum period. 54 Finally, both the concentric hypertrophy that occurs in the trained athlete who specializes in sports requiring isometric skeletal muscle .
One of the cardiac markers of target organ damage is left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) which can be easily diagnosed by echocardiography in clinical practice. With the widespread use of echocardiography, LVH is detected in a substantial number of patients with chronic hypertension. There are other techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging . RV hypertrophy in HCM is extremely heterogeneous, varying from mild concentric hypertrophy to more severe obstructive disease, either isolated or associated with LV hypertrophy. 12 RV hypertrophy is common in CA and may show an apical sparing pattern. 13, 14 In Anderson–Fabry disease (AFD), RV and LV hypertrophy are often associated. 15 Few .
qrs widening and repolarization abnormality
In 1952, Omega unveiled the series-produced Constellation, a family of watches originally destined for men fitted with calibre 354. Two salient features distinguished the first members of the .
mild lv hypertrophy|eccentric vs concentric lv hypertrophy



























